# Sync Vuex Store
Sync Store is an auxiliary module for synchronizing the data with the backend. Tasks can be queued in the localForage in case the Internet access is not available.
# Actions
The sync store provides following public actions:
# queue ({ commit }, task)
Queue network sync method. This is very similar to standard browser's fetch() call but the difference is that the network call is queued and executed when the Internet is available.
Example usage:
context
.dispatch(
'sync/queue',
{
url: config.stock.endpoint + '/check/' + encodeURIComponent(product.sku),
payload: {
method: 'GET',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
mode: 'cors',
},
product_sku: product.sku,
callback_event: 'store:stock/stockAfterCheck',
},
{ root: true },
)
.then(task => {
resolve({
qty: product.stock.qty,
status: product.stock.is_in_stock ? 'ok' : 'out_of_stock',
onlineCheckTaskId: task.task_id,
}); // if not online, cannot check the source of true here
});
The callback_event is emitted after the results are received from the server party.
The url can contain two dynamic variable placeholders that will be expanded to the actual values just before the execution:
- current user token- current cart id
An example URL with variables: http://localhost:8080/api/cart/totals?token=&cartId=
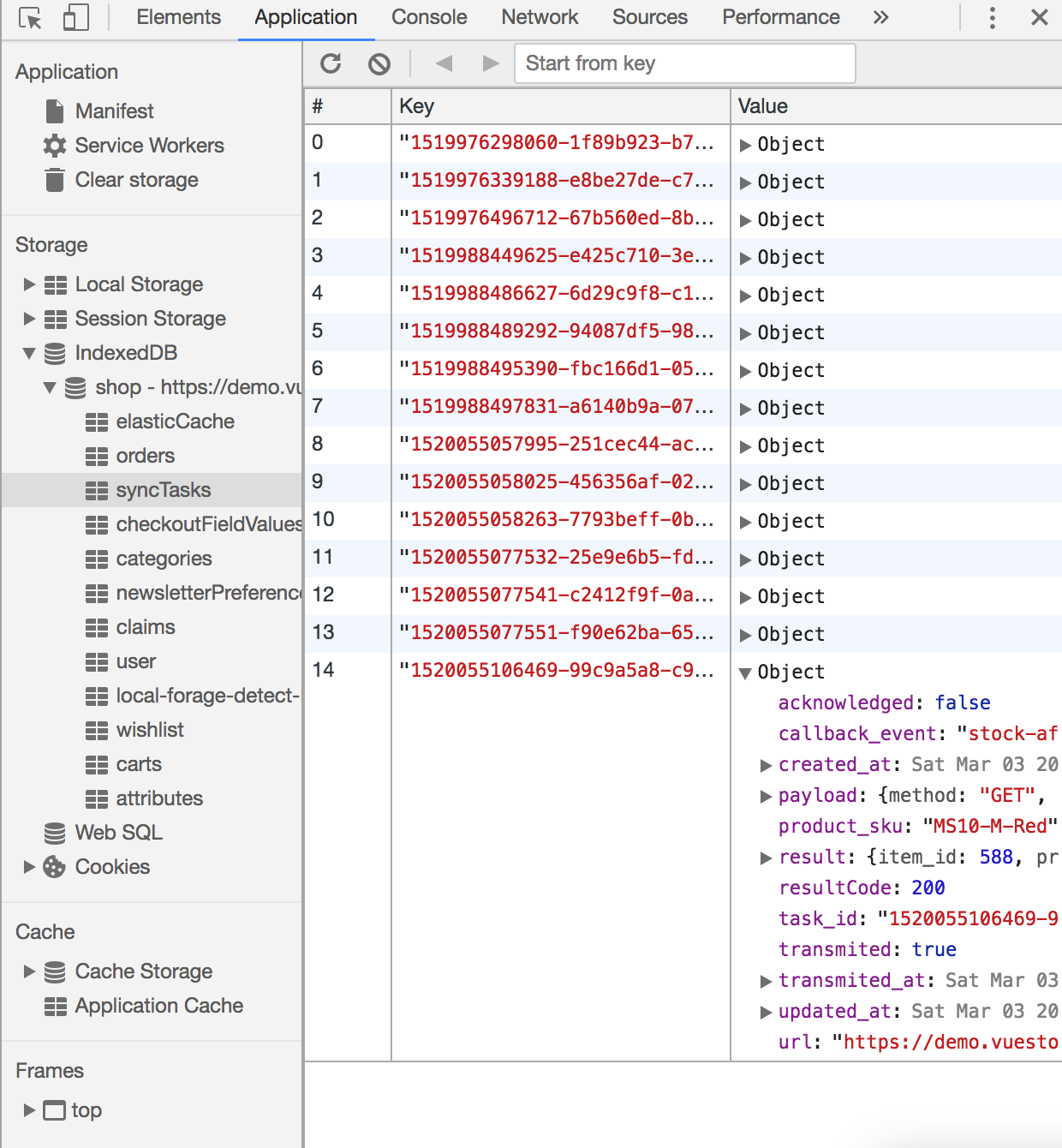
Note
The task object and then the results are stored within the syncTasks indexedDb/Local storage data table under the key of task.task_id
# Helpers
Some types of network calls shouldn't have been queued. For example the shopping cart synchronization or other tasks that operate on the volatile data/state.
In this case some modules (cart.js for example) do use just some helper methods from sync store to synchronize the data immediately but keeping the common interface for the network calls:
context
.dispatch(
'sync/execute',
{
url: config.cart.pull_endpoint, // sync the cart
payload: {
method: 'GET',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
mode: 'cors',
},
silent: true,
force_client_state: forceClientState,
callback_event: 'store:cart/servercartAfterPulled',
},
{ root: true },
)
.then(task => {});
sync/execute can be used as an equivalent of fetch().