Add Product to Cart
Just getting the data from the API is not enough. Ecommerce websites are feature rich and one of the most important features is the ability to add products to the cart. In this guide, we will learn how to add products to the cart in Alokai Next.js application.
Create Sdk context and hook
So far, we've been using getSdk to access the SDK on the server side. We can also use it on the client side.
However, this result in the SDK being reinitialized on every call. For better performance, we'll
create a context and hook to hold SDK instance.
First we need to export Sdk type from sdk.ts. Add this line at the end of the file.
+ export type Sdk = ReturnType<typeof getSdk>;
Next, we can define the SDK context and provider by creating apps/storefront/sdk/alokai-context.tsx file with the following content:
"use client";
import { createContext } from "react";
import { Sdk } from "./sdk";
export const SdkContext = createContext<Sdk | null>(null);
export function SdkProvider({
children,
sdk,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode;
sdk: Sdk;
}) {
return <SdkContext.Provider value={sdk}>{children}</SdkContext.Provider>;
}
Create an apps/storefront/providers/providers.tsx file that will aggregate all the providers. The file should have the following content:
"use client";
import { ReactNode } from "react";
import { SdkProvider } from "@/sdk/alokai-context";
import { getSdk } from "@/sdk/sdk";
export function Providers({ children }: { children: ReactNode }) {
return (
<SdkProvider sdk={getSdk()}>
{children}
</SdkProvider>
);
}
Now, add the Providers to the layout.tsx:
+ import { Providers } from "@/providers/providers";
import type { Metadata } from "next";
import { Inter } from "next/font/google";
import "./globals.css";
const inter = Inter({ subsets: ["latin"] });
export const metadata: Metadata = {
title: "Vue Storefront Next.js Starter",
description: "Vue Storefront Next.js Starter",
};
export default function RootLayout({
children,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode;
}): JSX.Element {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body className={inter.className}>
+ <Providers>
{children}
+ </Providers>
</body>
</html>
);
}
Next, create useSdk hook in apps/storefront/hooks/useSdk.ts:
import { SdkContext } from "@/sdk/alokai-context";
import { useContext } from "react";
export const useSdk = () => {
const contextSdk = useContext(SdkContext);
if (!contextSdk) {
throw new Error("useSdk must be used within a SdkProvider");
}
return contextSdk;
};
Add to Cart
First, let's understand the process of adding a product to the cart. When a user clicks on the "Add to Cart" button, the product is added to the cart by it's cartId. The cart is a collection of products that the user wants to buy. The cart is stored in the backend and the frontend communicates with the backend to add products to the cart.
In order to achieve this, we will use Alokai SDK's createCartEntry method. This sends a request to Alokai Middleware and the middleware will add the product to the cart.
But that's not all. Since we are building a real-world application, we need to have a cart in a global state. So, let's first do some preparation.
Preparation
We will create a new CartContextProvider component that will provide the cart to the entire application. We will also create a new useCart hook that will be used to access the cart from any component.
First, let's create a new CartContextProvider component. Create a new file inside storefront/providers/CartContextProvider.tsx and add the following code.
"use client";
import { useSdk } from "@/hooks/useSdk";
import { Cart } from "@vsf-enterprise/sap-commerce-webservices-sdk";
import { createContext, useEffect, useState } from "react";
export const CartContext = createContext<{
cart: Cart;
updateCart: (cart: Cart) => void;
}>({
cart: {} as Cart,
updateCart: () => {},
});
export default function CartContextProvider({
children,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode;
}) {
const [cart, setCart] = useState<Cart>({} as Cart);
const sdk = useSdk();
useEffect(() => {
async function getCart() {
let cartId = localStorage.getItem("cartId") ?? "";
let cart: Cart;
if (!cartId) {
const { data } = await sdk.sapcc.createCart({});
cart = data;
} else {
try {
const { data } = await sdk.sapcc.getCart({ cartId: cartId });
cart = data;
} catch {
const { data } = await sdk.sapcc.createCart({});
cart = data;
}
}
localStorage.setItem("cartId", cart.guid ?? "");
setCart(cart);
}
getCart();
}, []);
function updateCart(updatedCart: Cart) {
setCart(updatedCart);
}
return (
<CartContext.Provider value={{ cart, updateCart }}>
{children}
</CartContext.Provider>
);
}
This Provider has to be a client component, so we can use useState and useEffect hooks. We are using localStorage to store the cartId.
Now, let's create a new useCart hook. Create a new file inside storefront/hooks/useCart.ts and add the following code.
import { Product } from "@vsf-enterprise/sap-commerce-webservices-sdk";
import { useContext } from "react";
import { CartContext } from "../providers/CartContextProvider";
import { useSdk } from "./useSdk";
export default function useCart() {
const { cart, updateCart } = useContext(CartContext);
const sdk = useSdk();
async function addToCart(product: Product, quantity: number = 1) {
try {
await sdk.sapcc.createCartEntry({
cartId: cart.guid as string,
orderEntry: {
quantity: quantity,
product: {
code: product.code as string,
},
},
});
const { data } = await sdk.sapcc.getCart({
cartId: cart.guid as string,
});
updateCart(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error adding to cart", error);
}
}
return {
cart,
addToCart,
};
}
This hook will be used to access the cart and add products to the cart. We are using the useContext hook to access the cart from the CartContextProvider component and keeping the cart updated in the global state.
Now, let's add our new CartContextProvider to the provider.tsx file to wrap the entire application with the cart context.
+ import CartContextProvider from "./CartContextProvider";
export function Providers({ children }: { children: ReactNode }) {
return (
<SdkProvider sdk={getSdk()}>
+ <CartContextProvider>
{children}
+ </CartContextProvider>
</SdkProvider>
);
}
We need to keep CartContextProvider inside SdkProvider because we are using the useSdk hook inside the CartContextProvider.
Now, we can use the useCart hook to access the cart and add products to the cart from any component.
Add to Cart Button
Since ProductDetails component already has the product data and SfButton component that is responsible for adding the product to the cart, we can add the useCart hook to the ProductDetails component and use it to add the product to the cart.
// ... rest of the code
+ import useCart from "@/hooks/useCart";
export default function ProductDetails({ product }: ProductDetailsProps) {
const inputId = useId();
+ const { addToCart } = useCart(); // Add this line
const min = 1;
const max = product.stock?.stockLevel ?? 1;
const [value, { inc, dec, set }] = useCounter(min);
// ... rest of the code
Now, we can use the addToCart function to add the product to the cart when the user clicks on the "Add to Cart" button.
// ... rest of the code
<SfButton onClick={async () => await addToCart(product, 1)} size="lg" className="w-full xs:ml-4" slotPrefix={<SfIconShoppingCart size="sm" />}>
Add to cart
</SfButton>
// ... rest of the code
Now, when the user clicks on the "Add to Cart" button, the product will be added to the cart and the cart will be updated in the global state.
Let's test it!
Test it
Let's create a simple NavBar component with a Cart icon that will display the number of products in the cart. Create a new file inside storefront/components/NavBar.tsx and add the following code.
"use client"
import { SfBadge, SfButton, SfIconShoppingCart } from "@storefront-ui/react";
import Link from "next/link";
import useCart from "../hooks/useCart";
export default function NavBar() {
const { cart } = useCart();
return (
<div className="flex items-center justify-between px-8 py-3 bg-primary-700">
<nav className="flex gap-4 items-center">
<Link href="/" className="text-white">Home</Link>
<Link href="/cart" className="text-white">Cart</Link>
</nav>
<SfButton className="relative" square variant="tertiary">
<SfIconShoppingCart className="text-white" />
<SfBadge content={cart.totalUnitCount} />
</SfButton>
</div>
)
}
Now, let's add the NavBar component to the layout.tsx file.
// ... rest of the code
+ import NavBar from "../components/NavBar";
// ... rest of the code
<Providers>
+ <NavBar />
{children}
</Providers>
// ... rest of the code
Now, when the user adds a product to the cart, the number of products in the cart will be displayed in the NavBar component. The cart will be updated in the global state and the user will be able to see the number of products in the cart from any page.
Here's how it looks like:
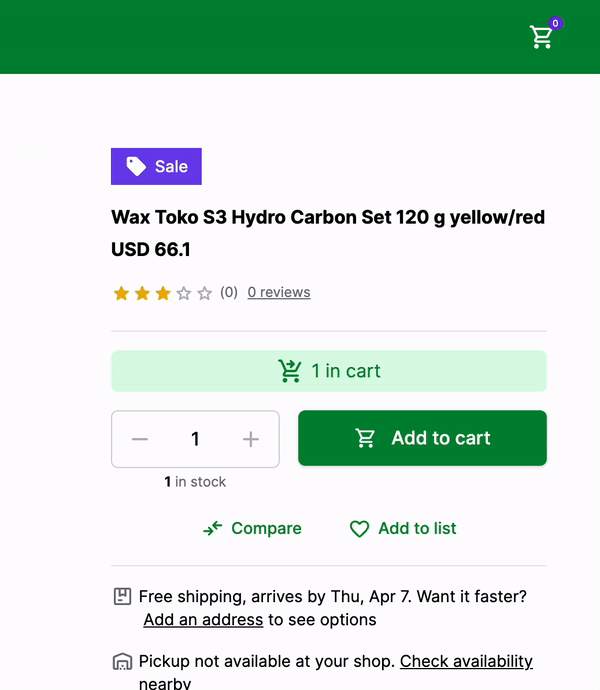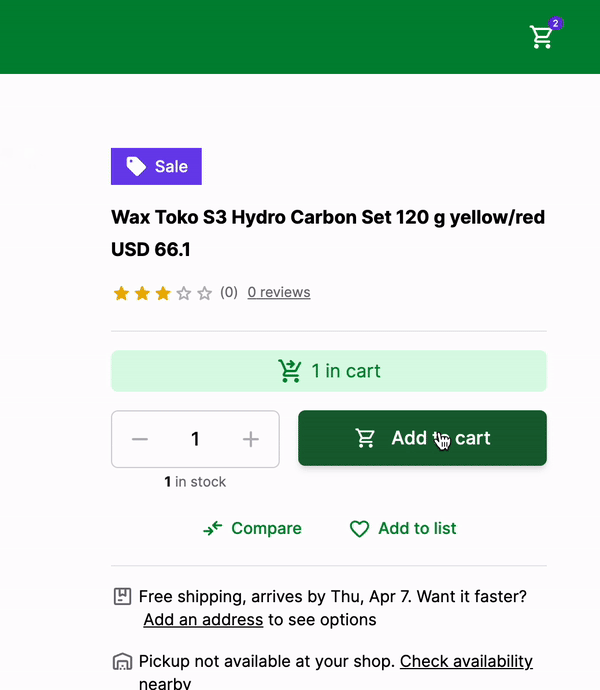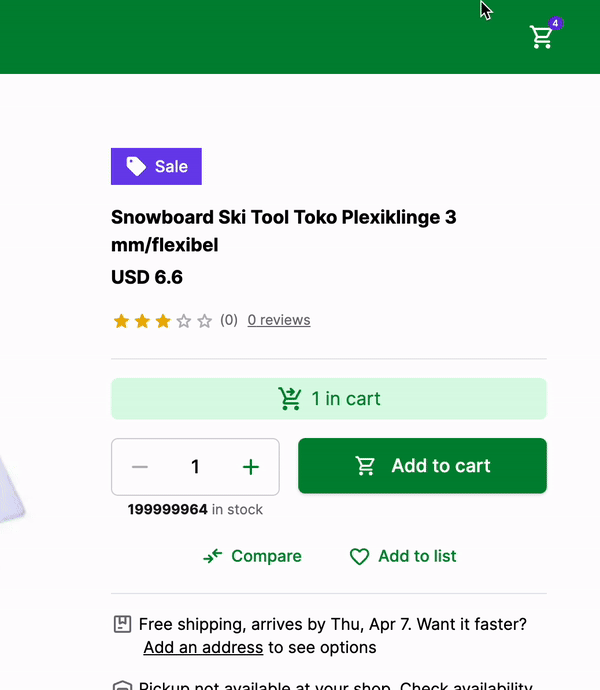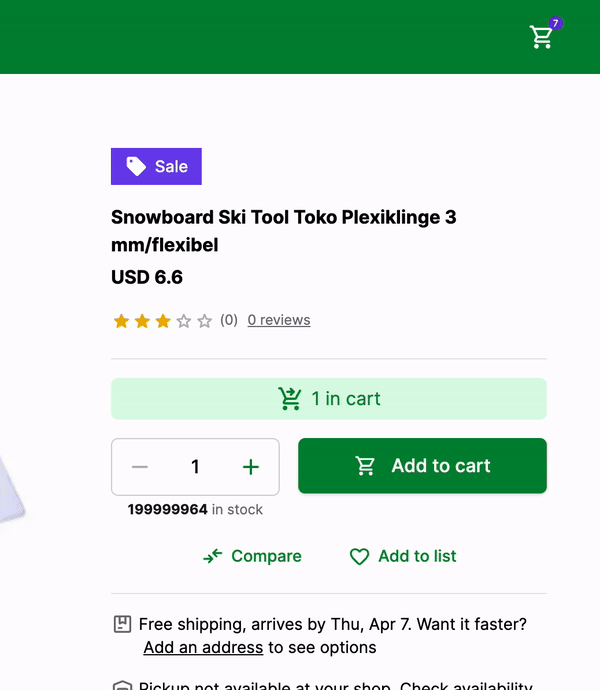
That's it! We have successfully added the product to the cart and displayed the number of products in the cart in the NavBar component.
Congratulations! You have successfully added products to the cart in Alokai Next.js application. 🎉
You can find a complete code for this guide in the add-to-cart branch of the Alokai Next.js Starter.
Summary
In this guide, we learned how to add products to the cart in Alokai Next.js application. We created a new CartContextProvider component that provides the cart to the entire application and a new useCart hook that is used to access the cart from any component. We also added the NavBar component that displays the number of products in the cart.
If you followed along with this guide, you might have noticed that we added Cart route to the NavBar component. You already know how to create a new page and display the products in the cart. If you want to challenge yourself, try to create a new page that displays the products in the cart and allows the user to remove products from the cart. I recommend using Product Card Horizontal Storefront UI component to display the products in the cart.
We are done with the basics of Alokai Next.js application.
You can now move on to the next guide to learn more advanced concepts and features of Alokai or start building your own Alokai Next.js application and come back later to learn more advanced concepts.