Unified Data Layer
The Unified Data Layer is an enterprise-only feature which means you need to have Alokai Enterprise License in order to be able to use it.
The Unified Data Layer (UDL) is a new concept introduced by Alokai. This is a layer in the Alokai Middleware and Storefront that allows for unification of data from different sources. The UDL provides a standardized way to interact with data, regardless of the eCommerce platform you're using. The UDL provides a structured way to manage this data, ensuring that regardless of the platform — be it Commercetools, SAPCC, or BigCommerce — the data is consistently represented.
Prerequisites
Before we proceed, please take your time and learn more about the UDL in the Unified Data Layer section of Storefront documentation.
UDL in Alokai Next.js Application
In order to help you understand Unified Data Layer better, let's add it to our Alokai Next.js application. This will allow us to connect our application to different eCommerce platforms preserving the same data structure and UI components.
If you don't have any other ecommerce platform installed - no worries, you can just follow this guide to have a better understanding of how UDL works.
Installation and Configuration
In order to install Unified Data Model, we need to install @vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc package. This package is a set of Unified API Extensions for SAP Commerce Cloud.
Configuring Alokai Middleware
Go to apps/middleware directory and install the @vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc package by running the following command:
npm install @vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc
Next, we need to extend Middleware to include Unified API Extension. First, let's create unifiedApiExtension extension object in the middleware.config.ts file:
import { createUnifiedExtension } from "@vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc";
import { ApiClientExtension } from "@vue-storefront/middleware";
export const unifiedApiExtension: ApiClientExtension = createUnifiedExtension(
{
normalizers: {
addCustomFields: [{}]
},
methods: {},
config: {
}
}
);
The unifiedApiExtension object is the result of calling createUnifiedExtension function. The createUnifiedExtension function is a factory function that accepts normalizers, methods, and config as arguments.
normalizersproperty allows you to control the normalization process - mapping eCommerce-specific data types to the Unified Data Model.methodsproperty allows you to override the default methods - functions that fetch data from eCommerce and pass it through the normalizers. Read more about it in the documentationconfigcontains additional configuration required by the given integration. We cover them below.
transformImageUrl
SAP Commerce Cloud stores image urls as relative paths but the storefront needs absolute paths to display images. transformImageUrl function is responsible for providing correct image url.
Add this transformImageUrl configuration in middleware.config.ts:
export const unifiedApiExtension: ApiClientExtension = createUnifiedExtension({
normalizers: {
addCustomFields: [{}],
},
methods: {},
config: {
+ transformImageUrl: (url: string) => {
+ return new URL(url, process.env.SAPCC_BASE_URL).toString();
+ },
},
});
This function adds base path to the image url. Base path comes from the environment variables.
In the .env file, add the following environment variable:
SAPCC_BASE_URL=[your SAP Commerce Cloud base URL]
defaultCurrency
Nearly all calls to SAP OCC API require the currency parameter. Thus we need to specify with what currency the application should start.
export const unifiedApiExtension: ApiClientExtension = createUnifiedExtension({
normalizers: {
addCustomFields: [{}],
},
methods: {},
config: {
transformImageUrl: (url: string) => {
return new URL(url, process.env.SAPCC_BASE_URL).toString();
},
+ defaultCurrency: "USD",
},
});
Adding the unified extension to the integration
Now, we need to add the unifiedApiExtension to the extensions array in the middleware.config.ts file:
export const integrations = {
- sapcc: {
+ commerce: {
location: '@vsf-enterprise/sapcc-api/server',
configuration: {
// ...
},
api: {
// ...
}
},
+ extensions: (extensions: ApiClientExtension[]) => [...extensions, unifiedApiExtension]
}
};
The final middleware.config.ts file should look like this:
require("dotenv").config();
import { createUnifiedExtension } from "@vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc";
import { ApiClientExtension } from "@vue-storefront/middleware";
export const unifiedApiExtension: ApiClientExtension = createUnifiedExtension({
normalizers: {
addCustomFields: [{}],
},
methods: {},
config: {
transformImageUrl: (url: string) => {
return new URL(url, process.env.SAPCC_BASE_URL).toString();
},
defaultCurrency: "USD",
},
});
export const integrations = {
commerce: {
location: "@vsf-enterprise/sapcc-api/server",
configuration: {
OAuth: {
uri: process.env.SAPCC_OAUTH_URI,
clientId: process.env.SAPCC_OAUTH_CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: process.env.SAPCC_OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET,
tokenEndpoint: process.env.SAPCC_OAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT,
tokenRevokeEndpoint: process.env.SAPCC_OAUTH_TOKEN_REVOKE_ENDPOINT,
cookieOptions: {
"vsf-sap-token": { secure: process.env.NODE_ENV !== "development" },
},
},
api: {
uri: process.env.SAPCC_API_URI,
baseSiteId: process.env.DEFAULT_BASE_SITE_ID,
catalogId: process.env.DEFAULT_CATALOG_ID,
catalogVersion: process.env.DEFAULT_CATALOG_VERSION,
defaultLanguage: process.env.DEFAULT_LANGUAGE,
defaultCurrency: process.env.DEFAULT_CURRENCY,
},
},
extensions: (extensions: ApiClientExtension[]) => [
...extensions,
unifiedApiExtension,
],
},
};
Next, let's prepare the Unified API Extension for the Alokai SDK. Create a new file inside middleware directory called types.ts and add the following code:
export type { Endpoints as UnifiedEndpoints } from "@vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc";
export * from "@vsf-enterprise/unified-api-sapcc/udl"
Endpoints type is needed for SDK to automatically generate type-safe methods based on the available endpoints.
The second line exports the Unified Data Layer so that the storefront uses the same data model version.
Great! Now we have successfully installed and configured the Unified Data Layer in our Alokai Middleware. Next, we need to configure Alokai SDK to use the Unified Data Layer.
Configuring Alokai SDK
To configure Alokai SDK with the Unified Data Layer, we need to change the SDK configuration. In storefront/sdk/sdk.ts, add the following code that uses the UnifiedEndpoints:
- import { sapccModule } from "@vsf-enterprise/sapcc-sdk";
+ import type { UnifiedEndpoints } from "middleware/types";
import { CreateSdkOptions, createSdk } from "@vue-storefront/next";
const options: CreateSdkOptions = {
middleware: {
apiUrl: "http://localhost:8181",
},
};
export const { getSdk } = createSdk(
options,
({ buildModule, config, middlewareModule, getRequestHeaders }) => ({
- sapcc: buildModule(sapccModule, {
+ unified: buildModule(middlewareModule<UnifiedEndpoints>, {
- apiUrl: config.middlewareUrl + "/sapcc",
+ apiUrl: config.middlewareUrl + "/commerce",
defaultRequestConfig: {
headers: getRequestHeaders(),
},
}),
})
);
export type Sdk = ReturnType<typeof getSdk>;
This code imports the UnifiedEndpoints type from the middleware/types file and uses it to create the unified module in the SDK configuration. The unified module uses the middlewareModule method to create a module based on the UnifiedEndpoints type.
Using Unified Data Layer in Alokai Next.js Application
Unified Data Layer brings a lot of benefits to the Alokai Next.js application. It allows us to use the same data structure and UI components across different eCommerce platforms. To use it though, your UI has to conform Unified Data Model structure.
If you try to run the application, you will see that we have an issue with the app/page.tsx file.
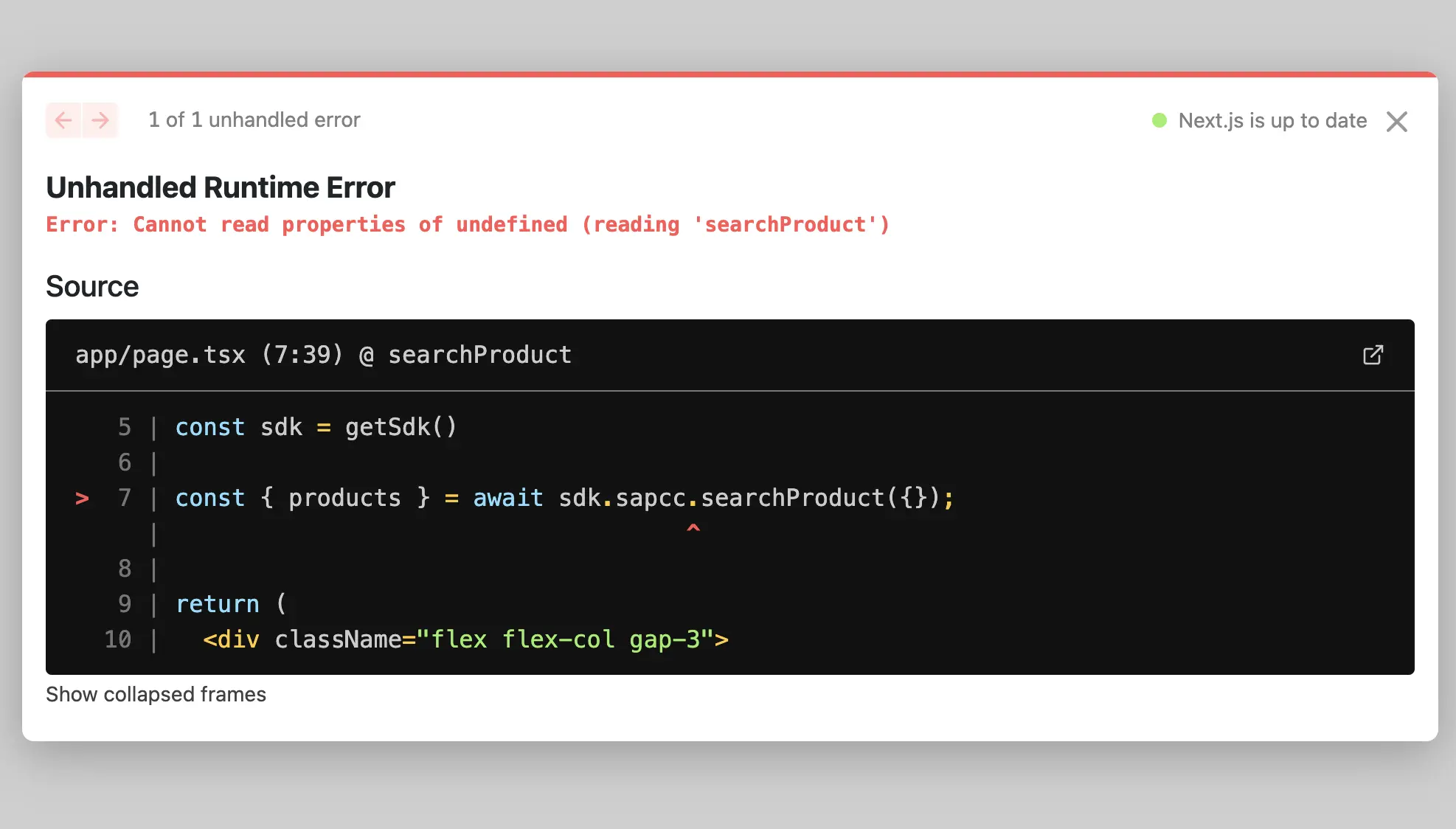
We are trying to use sdk.sapcc method, which doesn't exist anymore. Instead, we need to use sdk.unified method. Let's replace the sdk.sapcc method with the sdk.unified method:
import { getSdk } from "@/sdk/sdk";
import Link from "next/link";
const sdk = getSdk();
export default async function Page() {
- const { data: { products } } = await sdk.sapcc.getProducts({});
+ const { products } = await sdk.unified.searchProducts({});
return (
<div className="mx-auto px-6 py-4">
<h1>Product List:</h1>
<ul>
{products?.map((product) => (
- <li key={product.code} className="my-1">
+ <li key={product.id} className="my-1">
<Link
- href={`/product/${product.code}`}
- key={product.code}
+ href={`/product/${product.id}`}
+ key={product.id}
className="text-blue-500 underline"
>
{product.name}
</Link>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
Now, if you run the application, you will see that the home page is working as expected. However, if you try to navigate to the product details page, you will see that we have an issue.
Using Unified Data Layer in Product Details Page
Let's replace the types on the PDP with the Unified Data Model types. To do so, in the ProductDetails component, we replace the Product type with the SfProduct type from the Unified Data Model:
- import { Product } from '@vsf-enterprise/sap-commerce-webservices-sdk';
+ import { SfProduct } from "middleware/types";
interface ProductDetailsProps {
- product: Product;
+ product: SfProduct;
}
This change will allow us to use the same ProductDetails component across different eCommerce platforms.
Your IDE should show you a bunch of type errors in the ProductDetails component. Try figuring out how to fix the code yourself, it will help you get familiar with Unified Data Layer.
But if you're in hurry here's the final code for apps/storefront/components/ProductDetails.tsx:
"use client";
import {
SfButton,
SfCounter,
SfIconAdd,
SfIconCompareArrows,
SfIconFavorite,
SfIconPackage,
SfIconRemove,
SfIconSafetyCheck,
SfIconSell,
SfIconShoppingCart,
SfIconShoppingCartCheckout,
SfIconWarehouse,
SfLink,
SfRating,
} from "@storefront-ui/react";
import { clamp } from "@storefront-ui/shared";
import { ChangeEvent, useId } from "react";
import { useCounter } from "react-use";
import { SfProduct } from "middleware/types";
import useCart from "../hooks/useCart";
interface ProductDetailsProps {
product: SfProduct;
}
export default function ProductDetails({ product }: ProductDetailsProps) {
const inputId = useId();
const { addToCart } = useCart();
const min = 1;
const max = product.quantityLimit ?? 1;
const [value, { inc, dec, set }] = useCounter(min);
function handleOnChange(event: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) {
const { value: currentValue } = event.target;
const nextValue = parseFloat(currentValue);
set(Number(clamp(nextValue, min, max)));
}
return (
<section className="md:max-w-[640px]">
<div className="inline-flex items-center justify-center text-sm font-medium text-white bg-secondary-600 py-1.5 px-3 mb-4">
<SfIconSell size="sm" className="mr-1.5" />
Sale
</div>
<h1 className="mb-1 font-bold typography-headline-4">{product.name}</h1>
<strong className="block font-bold typography-headline-3">
<strong className="block font-bold typography-headline-3">
{product.price?.regularPrice.currency}{" "}
{product.price?.regularPrice.amount}
</strong>
</strong>
<div className="inline-flex items-center mt-4 mb-2">
<SfRating size="xs" value={product.rating?.average} max={5} />
<SfCounter className="ml-1" size="xs">
{product.rating?.count}
</SfCounter>
<SfLink
href="#"
variant="secondary"
className="ml-2 text-xs text-neutral-500"
>
{product.rating?.count} reviews
</SfLink>
</div>
<p
className="mb-4 font-normal typography-text-sm"
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: product.description ?? "" }}
/>
<div className="py-4 mb-4 border-gray-200 border-y">
<div className="bg-primary-100 text-primary-700 flex justify-center gap-1.5 py-1.5 typography-text-sm items-center mb-4 rounded-md">
<SfIconShoppingCartCheckout />1 in cart
</div>
<div className="items-start xs:flex">
<div className="flex flex-col items-stretch xs:items-center xs:inline-flex">
<div className="flex border border-neutral-300 rounded-md">
<SfButton
variant="tertiary"
square
className="rounded-r-none p-3"
disabled={value <= min}
aria-controls={inputId}
aria-label="Decrease value"
onClick={() => dec()}
>
<SfIconRemove />
</SfButton>
<input
id={inputId}
type="number"
role="spinbutton"
className="grow appearance-none mx-2 w-8 text-center bg-transparent font-medium [&::-webkit-inner-spin-button]:appearance-none [&::-webkit-inner-spin-button]:display-none [&::-webkit-inner-spin-button]:m-0 [&::-webkit-outer-spin-button]:display-none [&::-webkit-outer-spin-button]:m-0 [-moz-appearance:textfield] [&::-webkit-outer-spin-button]:appearance-none disabled:placeholder-disabled-900 focus-visible:outline focus-visible:outline-offset focus-visible:rounded-sm"
min={min}
max={max}
value={value}
onChange={handleOnChange}
/>
<SfButton
variant="tertiary"
square
className="rounded-l-none p-3"
disabled={value >= max}
aria-controls={inputId}
aria-label="Increase value"
onClick={() => inc()}
>
<SfIconAdd />
</SfButton>
</div>
<p className="self-center mt-1 mb-4 text-xs text-neutral-500 xs:mb-0">
<strong className="text-neutral-900">{max}</strong> in stock
</p>
</div>
<SfButton
onClick={async () => await addToCart(product, 1)}
size="lg"
className="w-full xs:ml-4"
slotPrefix={<SfIconShoppingCart size="sm" />}
>
Add to cart
</SfButton>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-center mt-4 gap-x-4">
<SfButton
size="sm"
variant="tertiary"
slotPrefix={<SfIconCompareArrows size="sm" />}
>
Compare
</SfButton>
<SfButton
size="sm"
variant="tertiary"
slotPrefix={<SfIconFavorite size="sm" />}
>
Add to list
</SfButton>
</div>
</div>
<div className="flex first:mt-4">
<SfIconPackage
size="sm"
className="flex-shrink-0 mr-1 text-neutral-500"
/>
<p className="text-sm">
Free shipping, arrives by Thu, Apr 7. Want it faster?
<SfLink href="#" variant="secondary" className="mx-1">
Add an address
</SfLink>
to see options
</p>
</div>
<div className="flex mt-4">
<SfIconWarehouse
size="sm"
className="flex-shrink-0 mr-1 text-neutral-500"
/>
<p className="text-sm">
Pickup not available at your shop.
<SfLink href="#" variant="secondary" className="ml-1">
Check availability nearby
</SfLink>
</p>
</div>
<div className="flex mt-4">
<SfIconSafetyCheck
size="sm"
className="flex-shrink-0 mr-1 text-neutral-500"
/>
<p className="text-sm">
Free 30-days returns.
<SfLink href="#" variant="secondary" className="ml-1">
Details
</SfLink>
</p>
</div>
</section>
);
}
Now, we need to pass the proper data to ProductDetails component. Apply the following changes to product/[id]/page.tsx file:
export default async function Page({ params }: { params: { id: string } }) {
const sdk = getSdk();
- const { data } = await sdk.sapcc.getProduct({
- productCode: params.id,
- });
+ const { product } = await sdk.unified.getProductDetails({
+ id: params.id,
+ });
return (
<div className="flex flex-col gap-8 md:gap-12 lg:gap-16 max-w-screen-xl m-auto px-4 md:px-8 lg:px-12 xl:px-16 py-8 md:py-12 lg:py-16 xl:py-20">
<section className="flex flex-col items-start gap-8 md:flex-row md:gap-4 xl:gap-6">
<ProductGallery />
- <ProductDetails product={data} />
+ <ProductDetails product={product} />
</section>
<ProductSlider />
</div>
);
}
Finally, if you run the application, you will see that both home page and product details page are working as expected. Except for one thing. If you try to add a product to the cart, you will see that we have an issue with the useCart hook - nothing happens when you click the "Add to cart" button.
As an additional exercise, you can use the approach we learned above to fix the useCart hook. As a starting point, you'll need to replace the addToCart method from the sapcc module with the addToCart method from the unified module and as well, you need to replace the Cart type with the SfCart type from the Unified Data Model. You can also find the solution here udl branch.
You can find more information about different Unified Api Methods in the Unified Cart Methods section of Storefront documentation.
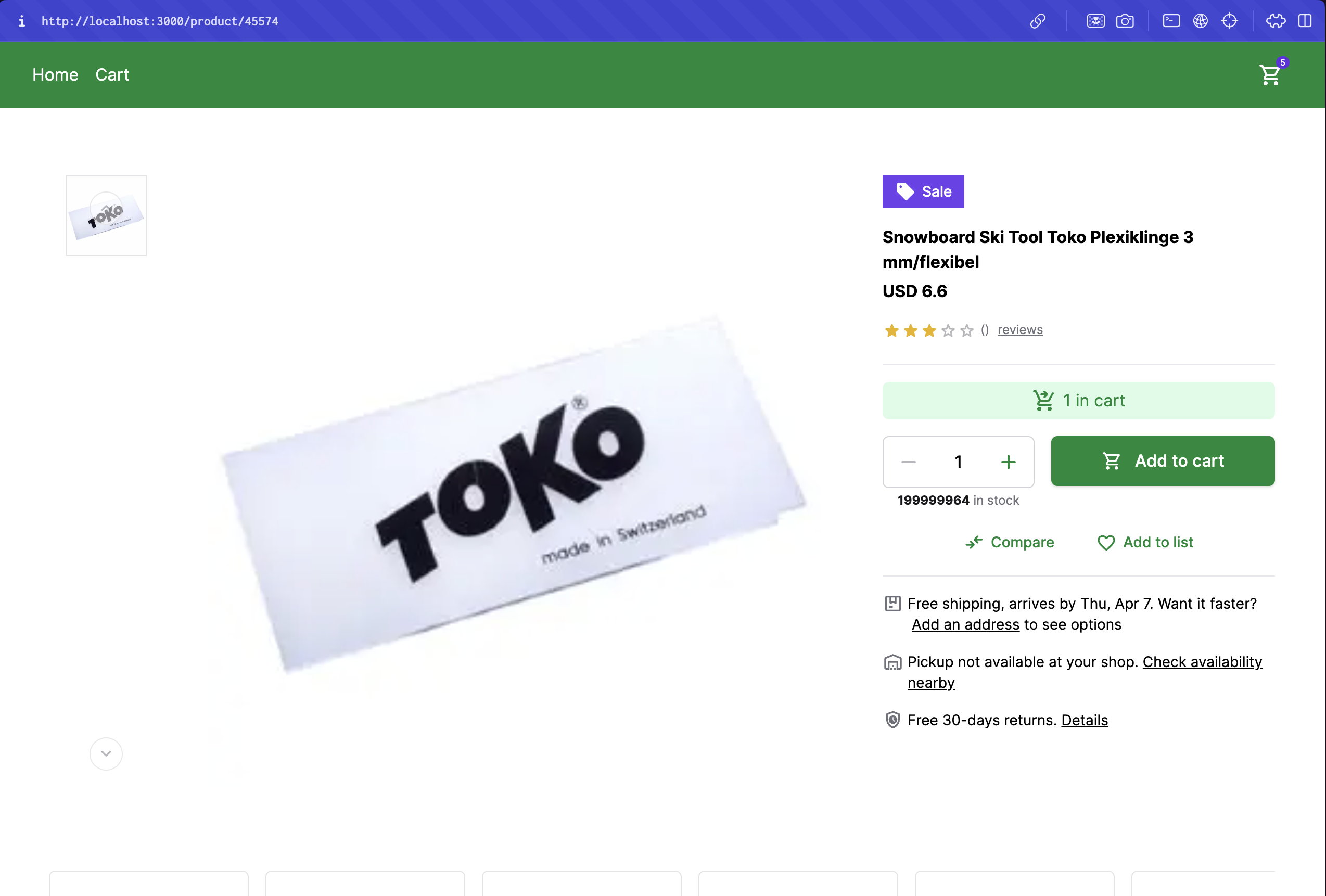
Displaying Images
So far, we've been displaying hardcoded images. But with the Unified Data Layer, we can easily access images from the e-commerce platform.
Open the storefront/components/ProductGallery.tsx file and add the following code:
// ... rest of the code
import { SfProduct } from "middleware/types";
interface ProductGalleryProps {
images: SfProduct['gallery'];
}
// ... rest of the code
In the above code, we have created a TypeScript interface ProductGalleryProps for the props of the ProductGallery Block. We have used the SfProduct type from the UDL.
Now, we will use the ProductGalleryProps interface to define the type of the props of the ProductGallery component. Replace the content of the storefront/components/ProductGallery.tsx file with the following code:
- export default function GalleryVertical() {
+ export default function GalleryVertical({ images }: ProductGalleryProps) {
We can also remove the images constant and withBase function from the ProductGallery component as we are now passing the images prop from the parent component.
Now, Replace all the occurrences of imageThumbSrc and imageSrc with url. The final shape of the ProductGallery component can be found in the udl branch.
Your IDE might throw a warning that we're using <img> instead of next/image. That's because we've copied the Gallery component from Storefront UI which is agnostic of a meta framework.
In production, it is recommended to use next/image.
Lastly, let's pass the images prop to the ProductGallery component in the app/product/[id]/page.tsx file. Replace the content of the app/product/[id]/page.tsx file with the following code:
- <ProductGallery />
+ <ProductGallery images={product.gallery} />
Conclusion
In this guide, we have learned how to add the Unified Data Layer to our Alokai Next.js application. We have successfully installed and configured Unified Data Layer in our Alokai Middleware and SDK. We have replaced the types across the application with the Unified Data Model types, and as well, we have fixed the errors across the application. We have learned how to use the same data structure and UI components across different eCommerce platforms. We also displayed product images.
As usual, you can find the final version of the application in the udl branch of the Next.js Starter repository.
In the next guide, we will learn how to extend Alokai application. How to override the existing methods, add new methods, and as well, how to create a new extension.