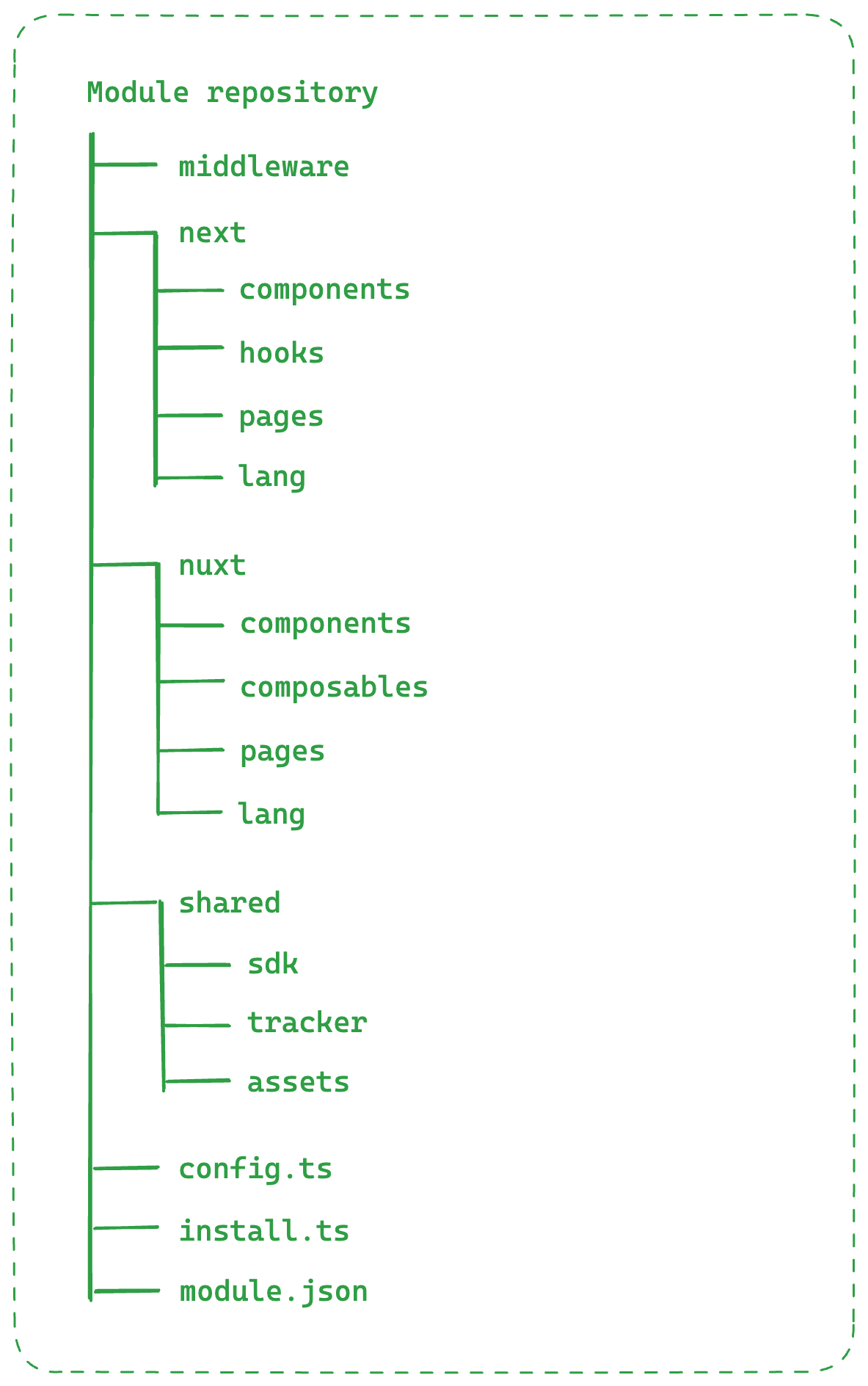
File structure
The module has to have a proper structure so CLI can read it properly and copy parts of modules in the right places.
The important directories in the module structure include:
- The
middlewaredirectory is the place with all files required by an extension you’re delivering through your module. - The
nextandnuxtdirectories containcomponents,hooks/composables,pages, andlangdirectories that are dedicated to the given frontend app. - The
shareddirectory contains all the files that are shared betweenNextandNuxtapplications. For exampleutilsorassets. - The
module.jsonfile with required properties so the module could work properly.
Module.json file
Each module should have its own module.json file that contains dependencies required by middleware and the frontend apps (accordingly for next & nuxt).
The CLI during the module installation adds the necessary dependencies to the package.json files in the apps.
The CLI will be installing modules by copying the files from the respective directories in the module into the applications. The module will be downloaded from the repository to the temporary folder or while using dev flag from a local directory.
Possible properties that can be used in the module.json file:
name(string) - full module name used as information for the user during installation through the CLI tool.supportedEcommerces(array) - array containing names of e-commerce that module support e.g['sapcc', 'sapcc-b2b'].dependenciesinsidenuxt,nextjs,middleware(object) - specific dependencies to work eithermiddlewareornextjs/nuxtapp can be defined here.
Example of module.json file:
{
"name": "SAP Checkout",
"nuxt": {
"dependencies": {
"lodash": "2.4.0"
}
},
"next": {
"dependencies": {
"lodash": "2.4.0"
}
},
"supportedEcommerces": [
"sapcc"
]
}
Installation script pattern
Currently, there are particular patterns baked inside CLI that are run when every module is installed.
Here's a list of all patterns that are run when the user installs a module with CLI arguments (e.g. add-module quick-order --dev="path-to-module/quick-order").
- The
middlewareareamiddlewaredirectory is copied intoapp/storefront-middleware/sf-modules/quick-order.modules.jsonpropertymiddleware.dependenciesobject is taken and merged withapp/storefront-middleware/package.json.
- The
nextjsareanextjsdirectory is copied intoapp/storefront-unified-nextjs/sf-modules/quick-order.nextjs/lang/{locale}.json(wherelocalecould be e.g.enorde) file is copied intoapp/storefront-unified-nextjs/lang/{locale}/{moduleId}.json(wheremoduleIdis module identifier in our casequick-order) and add import intoapp/storefront-unified-nextjs/lang/{locale}/index.tsas barrel import and then export all language files fori18n.modules.jsonpropertynextjs.dependenciesobject is taken and merged withapp/storefront-unified-nextjs/package.json.
- The
nuxtareanuxtdirectory is copied intoapp/storefront-unified-nuxt/sf-modules/quick-order.nuxt/lang/{locale}.json(wherelocalecould be e.g.enorde) file is copied intoapp/storefront-unified-nuxt/lang/{locale}/{moduleId}.json(wheremoduleIdis module identifier in our casequick-order) and add import intoapp/storefront-unified-nextjs/lang/{locale}/index.tsas barrel import and then export all language files viadefineI18nLocalefori18n.modules.jsonpropertynuxt.dependenciesobject is taken and merged withapp/storefront-unified-nuxt/package.json.
- The
sharedareashared/utilsdirectory is copied intoapp/storefront-unified-{nuxt,next}/sf-modules/quick-order/utils.shared/assetsdirectory is copied intoapp/storefront-unified-{nuxt,next}/public/quick-order.
Custom installation script instructions
In module installation script you can add custom logic containing copying over module files, doing changes to the users’ project, or initialization configuration. To ease the writing of the installation script, we’ve created module-kit package - please consult its readme. For examples of module installation scripts, please see modules repository.